Beta
The Neon Auth with Better Auth is in Beta. Share your feedback on Discord or via the Neon Console.
Neon Auth is built on Better Auth and provides full support for Email OTP plugin APIs through the Neon SDK. You do not need to manually install or configure the Better Auth Email OTP plugin.
Email OTP lets users receive a one-time password (OTP) by email and use it to:
- Sign in without a password
- Perform password resets
- Verify their email address (verification codes)
Neon Auth UI and Neon SDK are client-side SDKs, so you only invoke their methods. OTP generation and delivery are handled automatically - you do not have direct control over the codes sent to users.
Prerequisites
-
A Neon project with Auth enabled
-
Sign-up and Sign-in with Email enabled in your project's Settings → Auth.
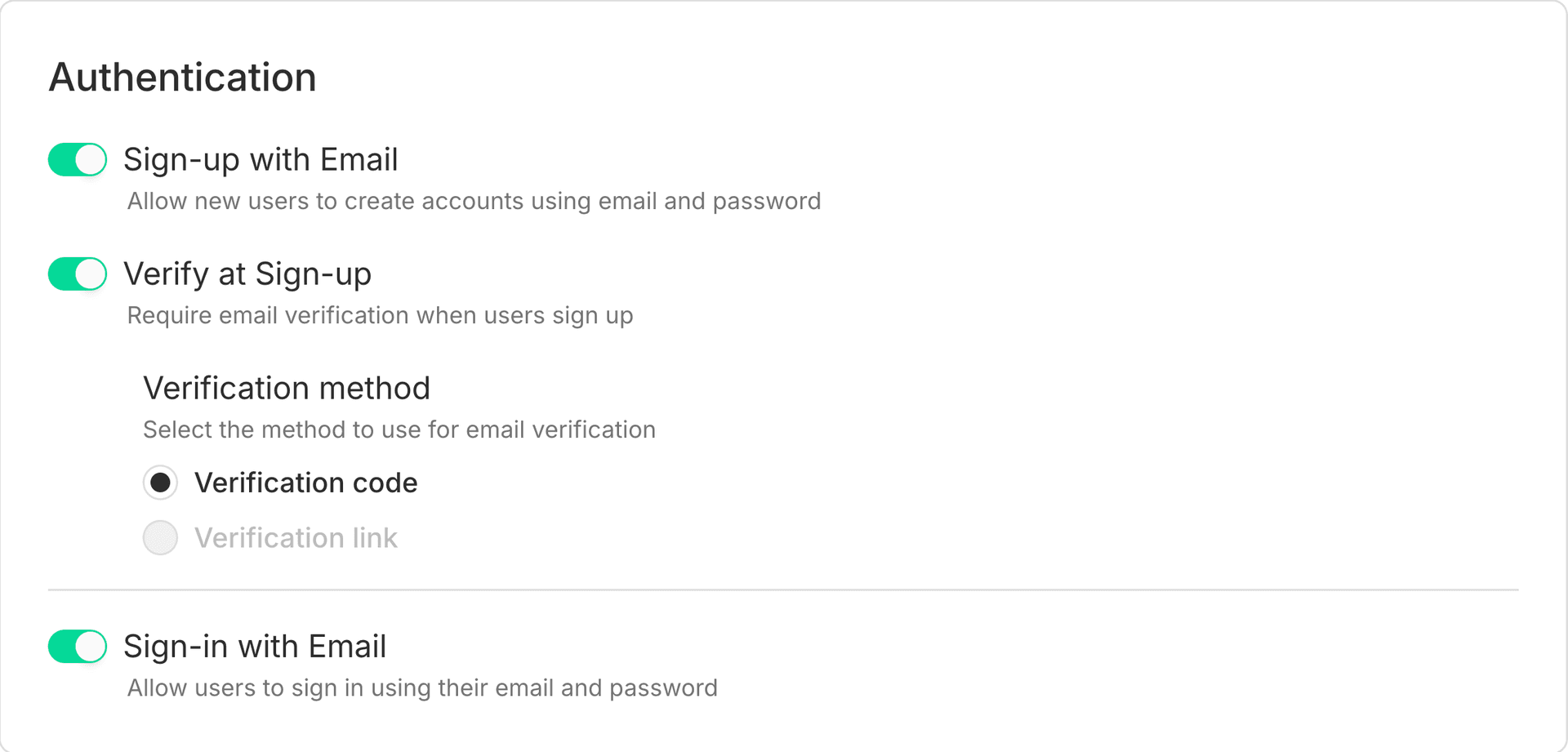
Email verification during sign-up
To use Email OTP for sign-up verification, enable Verify at Sign-up and select Verification code under Verification method.
Use Email OTP with UI components
If you're using Neon Auth UI components, enable Email OTP by passing the emailOTP prop to NeonAuthUIProvider. This enables OTP flows in the pre-built auth UI.
import { authClient } from '@/lib/auth/client';
import { NeonAuthUIProvider } from '@neondatabase/neon-js/auth/react/ui';
import './globals.css';
export default function RootLayout({ children }: Readonly<{ children: React.ReactNode }>) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body className={'antialiased'}>
<NeonAuthUIProvider
authClient={authClient}
emailOTP
>
{children}
</NeonAuthUIProvider>
</body>
</html>
);
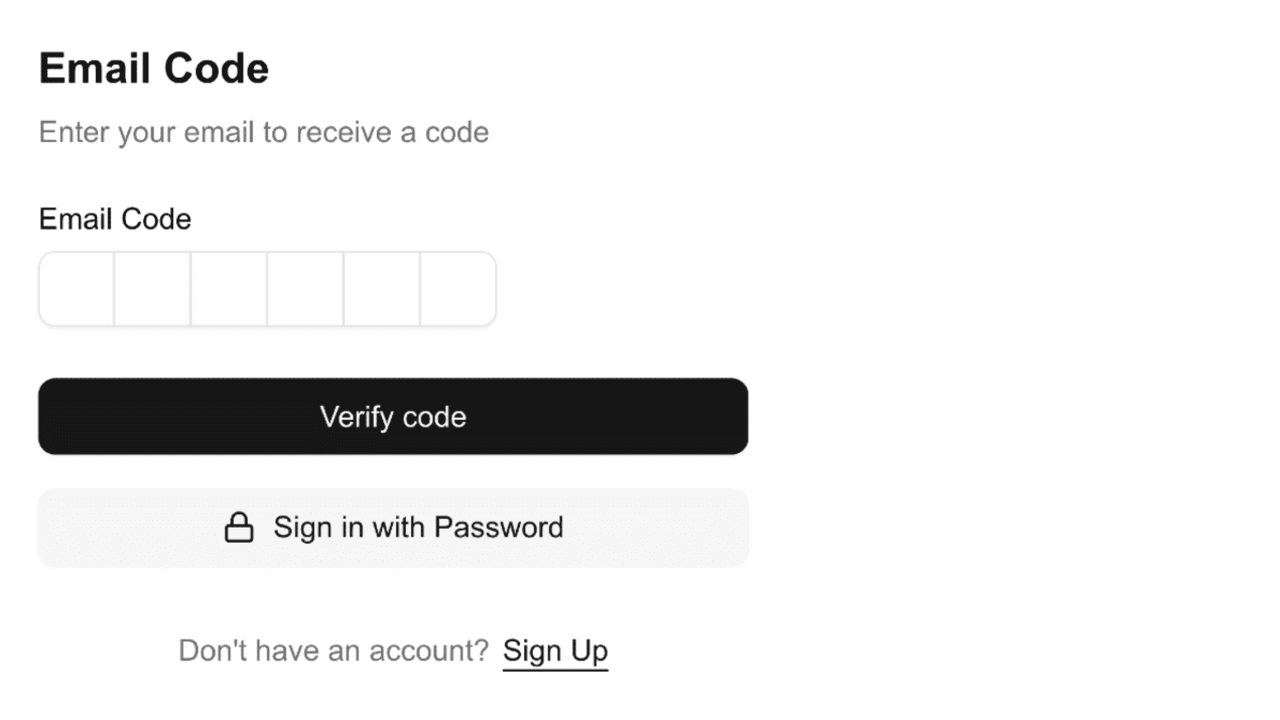
}Users can now sign in with Email OTP by selecting the option on the sign-in screen and entering the one-time code sent to their email.
If you haven't set up Neon Auth UI components yet, see our Quick start guides.
Use Email OTP with SDK methods
You can also implement OTP flows directly using the Neon SDK.
Send an OTP
To send an OTP, call emailOtp.sendVerificationOtp() and specify a type:
sign-in- passwordless sign-inemail-verification- verify an email address
import { authClient } from './auth';
export async function sendSignInOtp(email: string) {
const { error } = await authClient.emailOtp.sendVerificationOtp({ email, type: 'sign-in' });
if (error) throw error;
}For more details, see the Send verification OTP code in Neon SDK.
Sign in with OTP
After the user receives the code, sign them in using signIn.emailOtp():
import { authClient } from './auth';
export async function signInWithOtp(email: string, otp: string) {
const { data, error } = await authClient.signIn.emailOtp({ email, otp });
if (error) throw error;
return data;
}For more details, see the Sign in with OTP code in Neon SDK.
Verify email with OTP
If your project has email verification enabled with verification codes, Neon Auth sends an OTP during sign-up.
Once the user enters the code, verify the email address using emailOtp.verifyEmail():
import { authClient } from './auth';
export async function verifyEmail(email: string, otp: string) {
const { data, error } = await authClient.emailOtp.verifyEmail({ email, otp });
if (error) throw error;
return data;
}For more details, see the Verify email with OTP code in Neon SDK.
Checkout our Email verification guide for a complete walkthrough.
Check an OTP (optional)
If you want to validate an OTP without completing the flow (for example, to check the code before enabling a sensitive UI), you can use emailOtp.checkVerificationOtp():
import { authClient } from './auth';
export async function isOtpValid(email: string, otp: string) {
const { data, error } = await authClient.emailOtp.checkVerificationOtp({
email,
otp,
type: 'sign-in',
});
if (error) throw error;
return Boolean(data?.success);
}For more details, see the Check verification OTP code in Neon SDK.
Reset Password with OTP
You can also use Email OTP to implement password reset flows. To do this use the authClient.forgetPassword.emailOtp method to send a password reset OTP to the user's email address.
import { authClient } from './auth';
export async function sendPasswordResetOtp(email: string) {
const { error } = await authClient.forgetPassword.emailOtp({ email });
if (error) throw error;
}Once the user receives the OTP, verify it using authClient.emailOtp.checkVerificationOtp() with the type set to forget-password.
import { authClient } from './auth';
export async function verifyPasswordResetOtp(email: string, otp: string) {
const { data, error } = await authClient.emailOtp.checkVerificationOtp({
email,
otp,
type: 'forget-password',
});
if (error) throw error;
return Boolean(data?.success);
}Finally, reset the user's password using authClient.emailOtp.resetPassword():
import { authClient } from './auth';
export async function resetPasswordUsingOtp(email: string, otp: string, newPassword: string) {
const { data, error } = await authClient.emailOtp.resetPassword({
email,
otp,
password: newPassword,
});
}Limitations
Email OTP codes are time-limited and rate-limited.
If users exceed the allowed verification attempts, the API returns an error code like TOO_MANY_ATTEMPTS and the user must request a new code.
Email provider configuration
For production environments, we strongly recommend using a dedicated email provider. The default shared SMTP should be used only during development. Refer to the Email provider configuration guide for setup instructions.
Need help?
Join our Discord Server to ask questions or see what others are doing with Neon. For paid plan support options, see Support.