What you will learn:
Enable autoscaling for a compute
Configure autoscaling defaults for your project
Related topics
This guide demonstrates how to enable autoscaling in your Neon project and how to visualize your usage.
Did you know?
Neon's autoscaling feature instantly scales your compute and memory resources. No manual intervention or restarts are required.
Enable autoscaling for a compute
You can edit an individual compute to alter the compute configuration, which includes autoscaling.
To edit a compute:
-
In the Neon Console, select Branches.
-
Select a branch.
-
On the Computes tab, identify the compute you want to configure and click Edit.
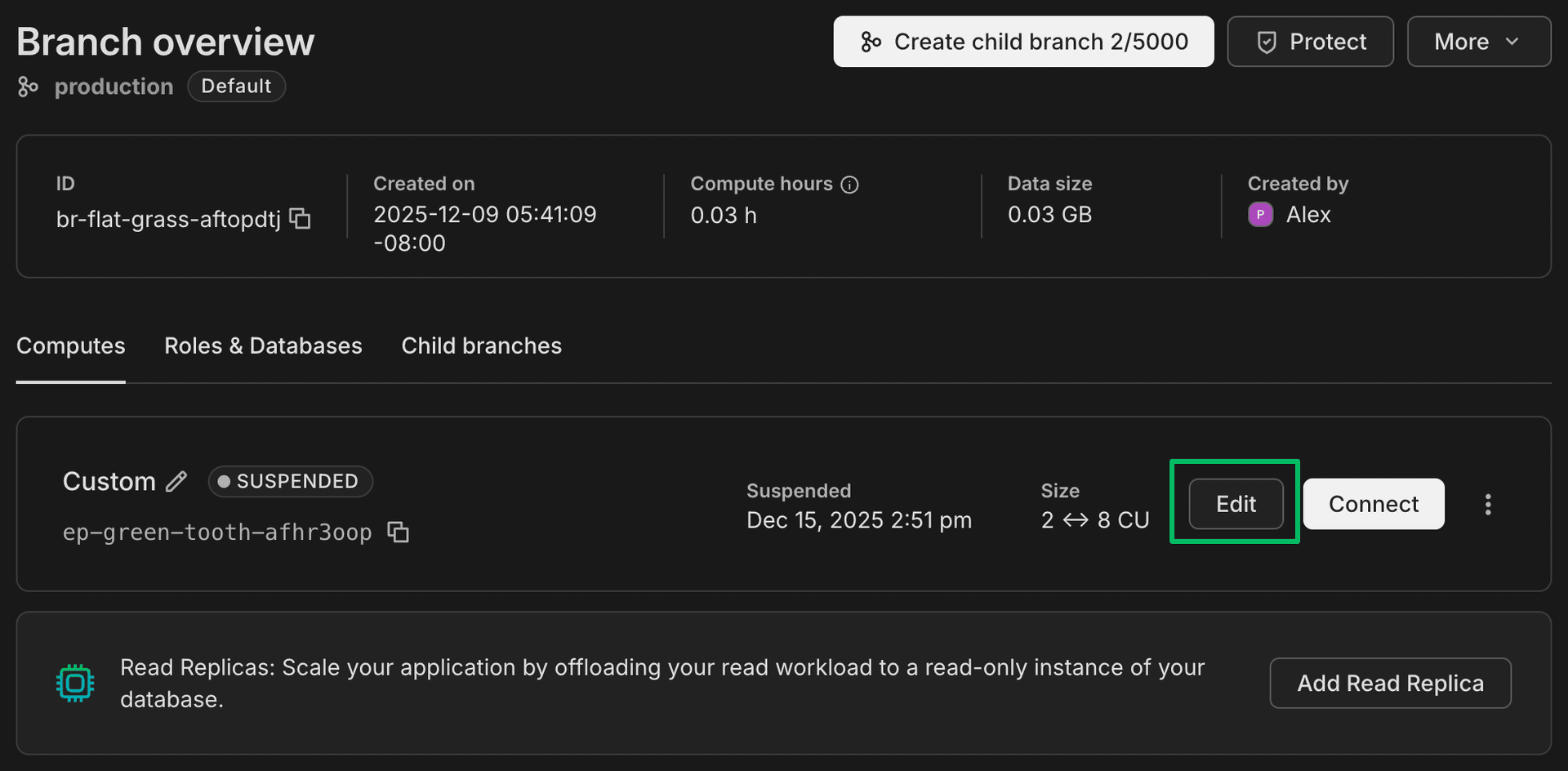
-
On the Edit compute drawer, select Autoscale and use the slider to specify a minimum and maximum compute size.
Neon scales the compute size up and down within the specified range to meet workload demand. Autoscaling currently supports a range of 1/4 (.25) to 16 CU. Each CU allocates approximately 4 GB of RAM — for example, 1 CU has 4 GB of RAM, 2 CU has 8 GB of RAM, and so on. For an overview of available compute sizes, see Compute size and autoscaling configuration.
note
The maximum permitted autoscaling range is 8 CU. This means the difference between your maximum and minimum compute size cannot exceed 8 CU. For example, if you set the minimum to 1 CU, the maximum can be at most 9 CU.
note
You can configure the scale to zero setting for your compute at the same time. For more, see Scale to Zero.
-
Click Save.
Configure autoscaling defaults for your project
You can configure autoscaling configuration defaults for your project so that newly created computes (including those created when you create a new branch or add read replica) are created with the same autoscaling configuration. This saves you from having to configure autoscaling settings with each new compute. See Change your project's default compute settings for more detail.
note
Changing your autoscaling default settings does not alter the autoscaling configuration for existing computes.
To configure autoscaling defaults:
- Navigate to your Project Dashboard and select Settings from the sidebar.
- Select Compute.
- Select Change to open the Change default compute settings modal.
- Use the slider to specify a minimum and maximum compute size and Save your changes.
The next time you create a compute, these settings will be applied to it.
Autoscaling defaults for each Neon plan
The following table outlines the initial default autoscaling settings for newly created projects on each Neon plan.
| Neon plan | Minimum compute size | Maximum compute size |
|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.25 | 2 |
| Launch | 0.25 | 8 |
| Scale | 0.25 | 8 |
Monitor autoscaling
From the Neon Console, you can view how your compute and RAM usage have scaled for the past 24 hours. On the Project Dashboard page, navigate down the page to the Monitoring section.
Some key points about this Autoscaling graph:
- Allocated refers to the compute and memory size provisioned to handle current demand; autoscaling automatically adjusts this allocation, increasing or decreasing the allocated compute and memory size in a step-wise fashion as demand fluctuates, within your minimum and maximum limits.
- CU Usage is represented by the blue line
- RAM usage is represented by the green line.
- A re-activated compute scales up immediately to your minimum allocation, ensuring adequate performance for your anticipated demand.
Place your cursor anywhere in the graph to get more usage detail about that particular point in time.
See below for some rules of thumb on actions you might want to take based on trends you see in this view.
Start with a good minimum
Ideally, for smaller datasets, you want to keep as much of your dataset in memory (RAM) as possible. This improves performance by minimizing I/O operations. We recommend setting a large enough minimum limit to fit your full dataset in memory. For larger datasets and more sizing advice, see how to size your compute.
Setting your maximum
If your autoscaling graphs show regular spikes that hit your maximum setting, consider increasing your maximum. However, because these spikes plateau at the maximum setting, it can be difficult to determine your actual demand.
Another approach is to set a higher threshold than you need and monitor usage spikes to get a sense of where your typical maximum demand reaches; you can then throttle the maximum setting down closer to anticipated/historical demand. Either way, with autoscaling you only use what's necessary; a higher setting does not translate to increased usage unless there's demand for it.
The neon_utils extension
Another tool for understanding usage, the neon_utils extension provides a num_cpus() function that helps you monitor how the Autoscaling feature allocates compute resources in response to workload. For more information, see The neon_utils extension.
Need help?
Join our Discord Server to ask questions or see what others are doing with Neon. For paid plan support options, see Support.